Rare Digital Art is a relatively new phenomenon and one of the new Blockchain efforts. This newer technology enables the creation of a unique market for Digital Art, which was previously considered virtually impossible.
Problems of (traditional) Digital Art
Traditional Digital Art is a form of art where artists use digital technology to create masterpieces. Examples of these creations include GIF, generated art, video, etc.
One of the main reasons why Digital Art sales are not growing as much as physical art today is because they lack uniqueness and authenticity. People are able to simply download traditional Digital Art and then claim it as their own. It can be difficult to prove the authenticity of digital artwork, especially after it has been distributed over the Internet.
There are millions of digital artists capable of creating this type of art. Most of them can only make money by selling services, or they can sell a physical copy of their creation as a framed print or t-shirt. This can be limiting, however, as it can be a bit difficult to put a GIF on a t-shirt.

The main advantages of Rare Digital Art
Rare Digital Art is a new art form where uniqueness and authenticity is guaranteed by blockchain technology. This allows the digital artist to combine their digital artwork, transactions, and identity information and then inextricably link them to a unique token. Once stored, the unique attributes cannot be changed.
The protocol called ERC-721 (see my earlier article on Predictable Antiques of the Future), built on Ethereum, makes issuing, trading, and owning digital assets very possible. The history of ownership of artworks in the origin can be traced and can therefore influence their current and future value. Finally, liquidity is accompanied by the ability to sell, trade, or freely ship works.
Ownership
Because Digital Art is linked to a unique token, collectors can now own it and store it in a digital wallet. If the token follows industry standards (like ERC-721), it is instantly accessible and can be sold on many markets and platforms.
This can attract digital collectors looking for unique (AI) generated items or paintings, and then leads to a healthy and open secondary market that increases the value of the artwork.
(Real) Limited Edition
Creators can now publish only a limited number of signatures and a (real) copy of their digital work, different from those available - for example - through a screenshot or right-click and save.
Again, the authenticity of the artwork is now publicly available and can be found in the blockchain where it was stored. Since this information cannot be altered, the creator or future collectors can ensure that its authenticity can always be proven.
Marketplaces and Brokers
Rare Digital Art Brokers such as OpenSea give a good idea of what is going on. All you have to do is scroll down on their website. You'll immediately discover a limited or unique number of digital artworks released by various mortal artists or AI.
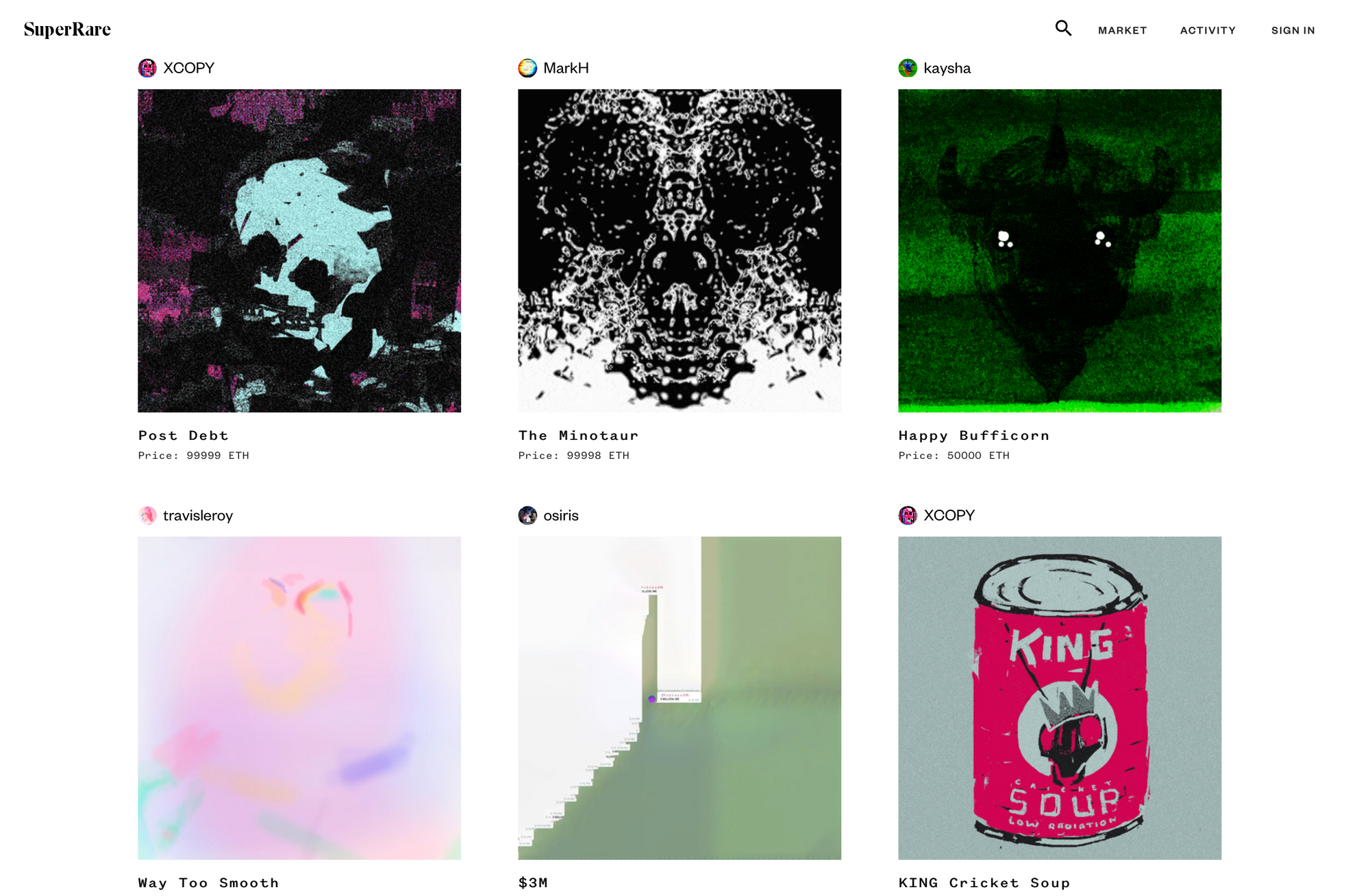
Super Rare
- SuperRare is a social platform that promotes the creation and collection of crypto art. Since its inception, SuperRare has worked closely with artists to address their needs - as well as those of collectors. On the platform, art can be purchased with ETH and uploaded for free, signed by a smart contract. SuperRare was founded by John Crain, Chief Executive Officer of SuperRare and Jonathan Perkins, Chief Product Officer of SuperRare.
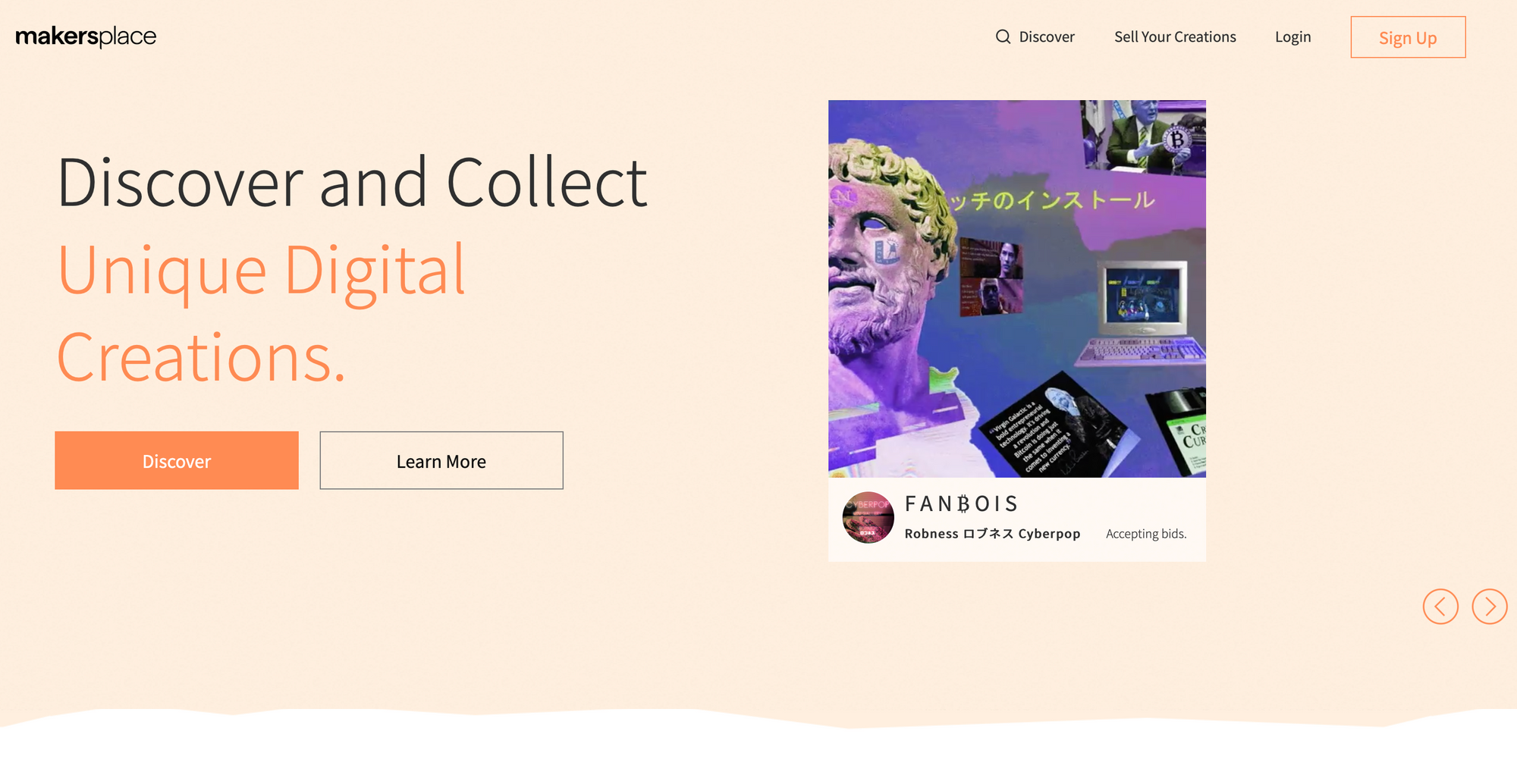
MakersPlace
- MakersPlace was founded by one of Pinterest's first employees. Similar to Etsy, the platform allows its artists to sell their works while the startup gets a 15% share. Collectors receive a non-fungible token (NFT) that represents ownership of a limited edition digital version of the product. The assets purchased can be stored in their own crypto wallet or in the MakersPlace wallet. The initial US$2 million seed round was led by Abstract Ventures, Draper Dragon Fund, and Uncork Capital, as well as angel investors from Pinterest, Facebook, Zillow, and Coinbase.

Certification and provenance
In the art world, there are many problems with fraud and proof of provenance. This makes art buyers skeptical and leads to an increasing demand for professional verification. This usually leads to an increase in the price of an artwork for all parties involved in the sale.
Blockchain technology is perfectly positioned to enable new levels of transparency. There are a handful of companies using blockchain technology to get an overview of the history of an artwork and provide irrefutable proof of ownership.
Certification
Verisart is a blockchain platform that helps users create secure digital certificates for art and collectibles. Using blockchain technology, they can link these works to detailed proofs of origin. Their goal is to create tamper-proof certificates of authenticity and ownership to prevent fraud and protect legitimate art trade.
Provenance
- FRESCO is a Swiss "trusted distribution platform" for artists, distributors and art organizations. Their trust token distribution mechanism is called the FRESCO protocol and allows their users to assign FRES tokens to each artwork, representing the potential value of the work, anonymously assigned by the owner and the community. The collaborative aspect of the platform is enabled by FRES Cash, which allows community members to assign their own values to other works. In this way, they lend credibility to the value of a work beyond the owner's assessment.
- Artory is used to register existing physical works of art. The Artory registry tracks the provenance of artworks and other collectibles using a blockchain ledger to ensure that chains of custody are authentic and tamper-proof. The registry provides security and anonymity for buyers and collectors. At the same time, it guarantees potential buyers that they have all the accurate information they need before making a purchase decision.
Final Thoughts
Back to the original question: Why should anyone pay for digital art when you can still copy the underlying digital file?
Digital Art has no original object in its origin, or nothing that can be safely locked away in a (tax-free) vault. This has long hindered the creation of a market for Digital Art. But now - enabled by blockchain technology - a unique cryptographic token can be linked to a digital file and secured in the blockchain. Someone can then buy and own that token and securely register all transactions, resulting in unique ownership and enabling (true) limited editions.
Recommended frames for displaying your collection of rare Digital Art:
- MEURAL Canvas; wonderful frame for Digital Art – other screen sizes available
- Samsung – The Frame (108 cm); other screen sizes available
- Samsung – The Serif (108 cm); other screen sizes available
The website and the information contained therein are not intended to be a source of advice or credit analysis with respect to the material presented, and the information and/or documents contained on this website do not constitute investment advice.

