Even the Templars, in a sense the first bankers, issued receipts to pilgrims for their deposited valuables (see: Big Think: "Did the Knights Templar invent modern banking?"). This refers to Christian pilgrims in Jerusalem. The city was taken in the First Crusade in 1099, and pilgrims began traveling thousands of miles across Europe.
These pilgrims somehow had to finance food, transportation, and lodging for months at a time, but avoided carrying large sums of cash or they would have become targets for robbers. The pilgrims could leave their cash at Temple Church in London and withdraw it in Jerusalem. Instead of carrying cash, pilgrims took a letter of credit. The Knights Templar were the Forex (FX) of the Crusades.
Even today, when a user holds assets with a third party - such as a bank - they are, by some sort of contractual agreement, legally their property, and on the bank's books, their assets are their liabilities - representing an obligation on their part to repay the user. Custodian banks actually only provide safekeeping of the assets deposited with them and their transfer.
Major banks have not remained idle and have now adapted to the online world. But one thing hasn't changed for them: They still own the users' money. Non-custodial (crypto) wallets ensure that users alone have control over their funds.
It is important to note that there are two types of crypto wallets - custodial solutions, where third parties, such as exchanges, have control over (crypto) currencies, and non-custodial solutions, where you have full control over your (crypto) currencies or digital assets. Let's take a closer look at the different solutions with some examples on the market.

Non-custodial wallets (decentralized)
While custodial wallets and exchange accounts hold your assets in their own accounts, non-custodial wallets give you full control over your assets.
Non-custodial: Users can send and transfer assets knowing that they are the only ones who have access to those assets.
Key-based: All non-custodial wallets have a unique key pair. This differs from centralized wallets as users are responsible for keeping their private keys secure, often introduced through a 12-word seed phrase.
Compatibility: Virtually all non-custodial wallets are accessible through a connection with a web3 wallet.
Advantages
Custodian of the private key: The user acts as the custodian - they simply act as "their own bank".
Transaction type: With non-custodial wallets, the transaction is (usually) reflected on the chain in real time.
- Security: The user owns the information, which reduces data theft due to a data breach.
- Offline Accessibility: Funding and related details are available offline.
Disadvantages
- Unlike custodial wallets that hold the private keys, the user cannot gain access by requesting the keys from a third party. The user is the only authority.
Examples of non-custodial wallets
(Most non-custodial wallets are interoperable with hardware wallets such as Ledger or Trezor).
Monolith
The company behind Monolith is "Token". Token is the trading name of Token Group Limited (a company registered in England and Wales (11098384). Its services are currently available in 31 different countries in Europe (EEA) and can also be accessed, for example, via a European IBAN number (or a UK sort code). Monolith users can order a VISA debit card (optional) free of charge through Monolith-GBP and EUR. The company does not charge a monthly fee, and users receive two free ATM withdrawals per month and a daily purchase limit of €7,600.
To use the services and the card, users must send cryptocurrencies to the company's fully decentralized, ERC-20-compliant smart contract wallet. The Company does not have access to the assets in the User's Wallet. The following cryptocurrencies are supported for token loading to the Visa Debit Card: ETH, TKN, DAI, DGD, DGX, MKR, SAI, USDT.
Additionally, the wallet itself supports: ABT, ANT, AOA, BAT, BIX; BNT, BTU, BZ, C20, CCCX, CENNZ, CRPT, DAI, DENT, DGD, DGTX, DGX.... and far more.
Other services include:
- Payment splitting: Users can split the cost of a purchase at a store among several of their crypto holdings by using the associated app.
Coin exchange: Market rates (best available rate) thanks to Monolith's DEX aggregator. The service also works with UniSwap, Kyber, Bancor, 0x, Mesh, and EtherDelta so far. - Open Source: The Smart Contracts for the token card are publicly available on Github.
- Fees: Monolith charges a 1% fee for topping up the debit card with cryptocurrencies and a 1% "community contribution" fee (or "license fee" when using their app) for each transaction as a contribution to the open source project.
- Monolith does offer a way to waive either fee, however. The first option is to load the card with DAI. In this case, the 1% deposit fee is waived (but you still have to pay the community contribution fee). DAI is a liquid stablecoin that you can easily buy on various exchanges. The second option is to use their TKN token. In this case, you will not pay a community contribution fee, but the 1% deposit fee will still be charged.
Project Community Chest: The community contribution fee will be automatically deposited into the project's community chest, which can be found at this Ethereum address. - For more information on fees, click here: "Fee Information Document"

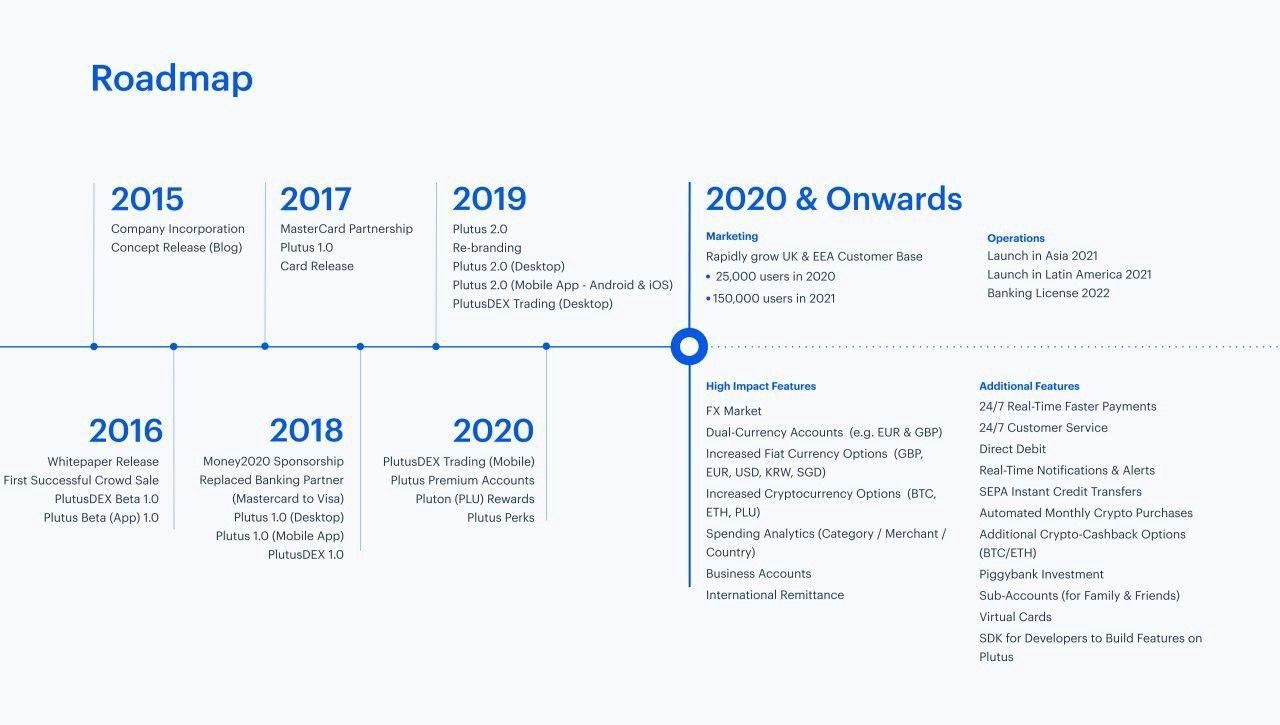
Plutus
Plutus is one of the longest running crypto card services, launched 2015. Their services are usable in nearly 200 countries, the VISA debit card provided (KYC required) can be loaded with GBP or EUR, with ETH and PLU currently the only cryptos supported. PLU is the startup's own loyalty token granted to users every time they use their debit card. A user can earn 3% crypto rewards in PLU and up to 15% cashback at select retailers (Nike, Vodafone, AirBnB, Skyscanner, etc.).
Once the user initiates a sell order on the decentralized exchange PlutusDEX, the order is matched and the user is prompted to send the money to the buyer using Metamask. This means that once you sell your cryptocurrency, the balance in GBP or EUR will be instantly credited to your account within the app. Of course, you also have the option to confirm or reject the current market rate.
Plus offers three different plans, which differ slightly in terms of limits and fees.
Limits (ab 25. Oktober 2020)
| Starter | Premium | Pro |
|---|---|---|
| £0.00/mo | £4.99/mo | £7.99/mo |
| Krypto-Handelslimits (£6.000 pro Monat) | Krypto-Handelslimits (£25.000 pro Monat) | Unlimitierter Handel |
| Limits für Kartenausgaben (£5.000 pro Monat) | Limits für Kartenausgaben (£15.500 pro Monat) | Limits für Kartenausgaben (£22.500 pro Monat) |
| Girokontostand Unbegrenzt | Girokontostand Unbegrenzt | Girokontostand Unbegrenzt |
| Keine PLU-Prämien | PLU-Prämien (3%) | PLU-Prämien (3%) |
| Kein Cashback | Cashback | Cashback |
Fees (As of: October 25, 2020)
| Starter | Premium | Pro |
|---|---|---|
| 1.75% trading fee, except PLU | 0% trading fee | 0% trading fee |
| £9.99 ticket order | Free ticket order | Free ticket order |
For more information, please visit the company's official website at Feeds & Limits.
Bitwala
Bitwala was one of the first platforms to offer both banking and a non-bailable crypto wallet and trading service. Bitwala's investors include Earlybird, Sony Financial Ventures, coparion, Global Brain, High Tech Gründerfonds, ALSTIN Capital and Digital Currency Group. The Berlin-based company also offers a Mastercard debit card for payments in stores and online. The offer is currently only available to EU citizens and can be used for salary payments, money transfers, standing orders and transfers to any bank within the EU. In return, they are protected up to €100,000 by the German deposit guarantee system.
Bitwala currently supports BTC and ETH and offers a "Bitwala Interest Account." Users can earn up to 5% interest on bitcoin deposits. Fees are very low (e.g. EUR 0.00 for account opening and maintenance, SEPA transactions, card payments in € in SEPA area, ATM withdrawals in SEPA area). For buying and selling cryptocurrencies, 1% of the transaction volume + a network fee is charged. A detailed price list can be found on their official website (PDF).
Custodial wallets
Custodial wallets are usually software wallets or wallets in digital exchanges where the private keys are held by a third party. This means that the third party has full control over your funds, while the user must give permission to send or receive payments. One drawback could be that the digital exchange or service provider could be hacked and the private keys stolen, which could result in the user losing 100% of their assets. To explain this in more detail, let's take a closer look at the advantages and disadvantages:
Advantages
- Free transactions: Unlike regular wallets, custody wallets do not charge a transaction fee. This means that customers can make transactions within the ecosystem for free.
- No major repercussions if private keys are lost: Even if users lose their private keys, it would be relatively easy to regain access to their wallet and stored values.
- Higher backup capability: Another advantage of custodial wallets is that the central authority that manages your wallet provides backup capabilities. This makes it easier to undo any transaction or restore a previous version.
Disadvantages.
- The custodian has control over the assets: The user has no autonomy over their wallet. The third party provider (custodian) has complete control over the assets and related processes. This may, for example, result in the user's freedom being restricted by freezing the account or the amount stored.
- Necessity of KYC: Performing KYC (Know Your Customer, ID verification) is critical for custodial wallets. Without proof of identity, users cannot access their assets or related services. This need for identity verification hinders the basic principles of anonymity.
- No offline capability: An Internet connection is required to log into custodial wallets or conduct transactions.
- Privacy breach threat: A large portion of users' funds are stored in cold and hot wallets. Even though the wallets themselves cannot be hacked, they are still vulnerable to security breaches.
Custodial wallet examples.
Since this article focuses on non-custodial solutions on the market, we will only briefly mention a few companies that offer custodial wallets: Bankera, Blockcard, Coinbase Card, Crypto.com, Fold Card, Nexo Card or Wirex Card
Final Thoughts
Non-custodial wallets are able to avoid the regulatory burdens that centralized custodial products must deal with (whether KYC, AML, MTL, etc.). In addition, there is no friction from government-issued IDs, SSNs, etc. Users can maintain much of their privacy and not have to worry about their sensitive data being hacked, compromised, or shared. Ultimately, this gives them absolute control and custody - users can become their own bank.
The website and the information contained therein are not intended to be a source of advice or credit analysis with respect to the material presented, and the information and/or documents contained on this website do not constitute investment advice.

